Compact
myelin of the central nervous system (CNS) contains a high proportion
of lipid (ca. 70 %) and several proteins, which are highly enriched in,
or specific to, myelin. The highly hydrophobic transmembrane
proteolipid protein, (PLP), and the extrinsic, hydrophilic myelin basic
protein (MBP), are the major myelin proteins of the CNS accounting for
approximately 40 % and 30 %, respectively of total protein. Although
the myelin proteins are largely conserved across species, our initial
investigations have shown that while similar to other well-defined
myelin proteins ( e.g. bovine, human, rat, murine) equine myelin has
some distinct differences.
This work is primarily concerned with PLP, which is one of the most
hydrophobic proteins in nature, and its DM20 isoform, which differs
from PLP by the insertion of an additional
35 amino acid cytoplasmic domain near the centre of the protein. In
PLP, the 276 amino acid polypeptide are thought to be structured into
four hydrophobic, membrane spanning, and five
hydrophilic domains (see below).
PLP and DM20 are both involved in the formation of the intraperiod
line (IPL), which is essential to the correct architecture of the
myelin sheath. Both proteins are implicated in
axon/glial interactions and patients lacking PLP and/or DM20 develop
axonopathy. Mutations of the X-linked PLP gene cause the neurological
disorders Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease (PMD)
and Spastic Paraplegia type 2 (SPG2) and similar disorders in a variety
of animals . A current conundrum is how to link the molecular defects
with the heterogeneous phenotypes. This
task would be simplified if we understood the 3-dimensional structures
that PLP and DM20 adopt in the oligodendrocyte membrane.
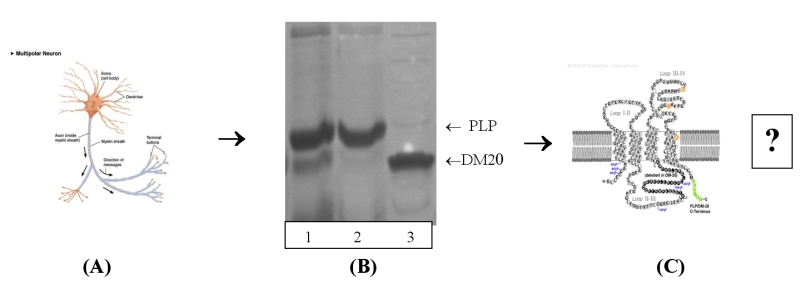
[Click image for larger version]
Figure shows :
(A) Nerve cell with the axon coated in myelin sheath.
(B) Extraction and purification of the equine transmembrane proteins PLP and DM20.
(C) Postulated proteolipid transmembrane structure – is this the true structure?
PLP and its DM20 isoform.
To
date most of our work is focussed on the extraction and purification of
these transmembrane proteins using specific detergents to solubilize
the lipid bilayer without compromising the structural integrity of the
proteins. Interestingly, we routinely extract PLP and DM20 as
individual components and also as a complex. Currently, we are
conducting crystallization trials on all three entities. (Shown above
on SDS-PAGE, 1: PLP/DM20 complex, 2: PLP and 3: DM20) We are trying to
correlate the protein profiles which are obtained from detergent
solubilised samples obtained from transgenic mice with and without
mutations collected over different life time spans.
Relevant publications:
Dominic J.B. Hunter, Rachel Macmaster, Aleksander W. Roszak, Alan Rimbaldi-Tunnicliffe, Ian R. Griffiths and A. Freer . (2005) Structure of myelin P2 protein from Equine Spinal Cord. Acta Cryst D61 , pp1067-1071.
McLaughlin M., Hunter D., Thompson C., Yool D., Kirkham D., Freer A. & Griffiths I.(2002) Evidence for possible interactions between PLP and DM20 within the myelin sheath. Glia, 39 , Issue 1, pp 31-36.
Wood D, She Y, Freer A , Harauz G. & Moscarello A. (2002) Primary structure of equine myelin basic protein by mass spectrometry. Arch. Biochem. & Biophys . 405 , pp 137-146.